

John Zhu
Position Velocity & Acceleration
Slide Duration:Table of Contents
11m 26s
- Intro0:00
- Definition0:28
- Properties: Vertical Line Test1:32
- Domain1:38
- Range1:59
- Vertical Line test2:19
- Example 12:33
- Example 23:10
- Properties: Roots or Zeros4:04
- Finding the Root4:16
- Properties: Forms5:12
- Graphically5:20
- List5:46
- Equation6:11
- Function6:38
- Properties: Odd & Even7:12
- Even Function7:14
- Odd Function8:25
- Properties: Increasing & Decreasing9:17
- Increasing Function9:22
- Decreasing Function10:21
13m 58s
- Intro0:00
- Manipulating0:10
- A in the Equation0:39
- B in the Equation0:44
- C & D in the Equation0:49
- Negative values0:59
- Example 11:17
- Example 21:51
- Example 3: Absolute Value Functions3:43
- Example 44:57
- Example 56:17
- Example 68:02
- Example 79:10
- Example 811:02
- Example 911:47
6m 47s
- Intro0:00
- Inverse0:08
- Definition0:18
- Example: Finding the Inverse1:03
- Example 22:29
- Example 33:12
- Example 44:41
5m 4s
- Intro0:00
- Types of Functions: Polynomials0:07
- No Domain Restrictions0:12
- No Discontinuities0:19
- Degree Test0:31
- Types of Functions: Polynomials1:17
- Leading Coefficient Test1:33
- Leading Coefficient Positive, Even Degree1:54
- Leading Coefficient Positive, Odd Degree2:13
- Leading Coefficient Negative Even Degree2:34
- Leading Coefficient Positive, Odd Degree2:46
- Examples: Types of Functions: Polynomials3:03
- Examples: Types of Functions: Polynomials4:18
6m 45s
- Intro0:00
- Types of Functions: Trigonometric0:05
- 6 Functions To Be Familiar With0:14
- Example 1: SIN1:38
- Example 2: COS3:22
- Example 3: TAN4:38
5m 58s
- Intro0:00
- Types of Functions: Trigonometric- Inverse Trig Functions0:07
- Example: Inverse SIN of X0:45
- Example: Inverse Function2:30
- Example: Inverse TAN of X4:42
17m 42s
- Intro0:00
- Types of Functions: Trigonometric- Trig Identities0:07
- 4 Identities0:24
- Pythagorean0:28
- Double Angle1:10
- Power Reducing1:28
- Sum or Difference1:42
- Couple More Identities1:59
- Negative Angle2:04
- Product to Sum2:39
- Example 1: Prove3:00
- Example 2: Simplify Expression5:02
- Example 3: Prove5:56
- Example 4: Prove8:02
- Example 5: Prove With TAN12:43
5m 53s
- Intro0:00
- Types of Functions: Exponentials0:07
- General Form0:10
- Special Exponential Function0:17
- Example 1: Using Exponential Properties0:46
- Example 2: Using Exponential Properties1:58
- Example 3: Using Trig Identities & Exponential Properties3:16
- Example 4: Using Exponential Properties4:37
7m 8s
- Intro0:00
- Types of Functions: Logarithmic0:06
- General Form0:10
- 2 Special Logarithmic Func.0:19
- Euler's # / Natural Log0:27
- Logarithmic & Exponential Relationship0:45
- Log form1:56
- Properties2:09
- Example 1: Apply Basic Principle of Log Func.3:05
- Example 2: Use Properties3:40
- Example 3: Regular Log5:16
15m 36s
- Intro0:00
- Types of Functions: Rational - Definition0:06
- Example 1: Graph Rational Func.0:36
- Example 2: Find Asymptotes of Func.7:02
- Example 3: Find Asymptotes of Func.8:59
- Example 4: Graph Rational Func.11:08
14m 58s
- Intro0:00
- Types of Conic Sections0:06
- Parabolas0:19
- Circles1:36
- Ellipses2:40
- Hyperbolas4:42
- Complete the Square6:40
- Example: Conic Sections9:08
- Example 2: Conic Sections10:59
- Example 3: Graph Conic Sections12:21
7m 15s
- Intro0:00
- Definition0:06
- Example: Limit0:17
- Properties1:13
- 1st Property1:21
- 2nd Property1:34
- Special Property1:51
- Limits2:36
- Explain Example2:49
- Limits Example4:39
- Limits Example5:21
8m 1s
- Intro0:00
- Solving Limits with Algebra0:07
- Example 1: Solve Algebraically0:30
- Solving Limits with Algebra, Example 22:28
- Solving Limits with Algebra, Example 33:18
- Solving Limits with Algebra, Example 44:56
- Solving Limits with Algebra, Example 56:26
3m 16s
- Intro0:00
- Rational Limit Rules0:07
- Review of Solving Problem Algebraically0:08
- Limit Rules0:28
- Rule 10:35
- Rule 20:40
- Rule 30:45
- Rational Limit Rules1:02
- Applying 1st Rule1:22
- Rational Limit Rules1:50
- Applying 2nd Rule2:09
- Rational Limit Rules2:26
- Applying 3rd Rule2:40
9m 57s
- Intro0:00
- Types of Limits: One-Sided Limit Rules0:06
- Example0:19
- Applying Same Rule0:34
- Rule to Keep In Mind0:52
- Types of Limits: One-Sided Limit Example 11:12
- Limit of x² From Negative Side2:11
- Types of Limits: One-Sided Limit, Example 22:27
- Types of Limits: One-Sided Limit, Example 34:26
- Types of Limits: One-Sided Limit, Example 45:47
- One-Sided Limit Example: X with Even Degree Polynomial7:00
- One-Sided Limit Example: Entire Denominator Squared8:09
8m 28s
- Intro0:00
- Types of Limits: Special Trig Limits0:07
- Pre-set Rules0:35
- Special Trig Limits, Example 10:58
- Special Trig Limits, Example 22:50
- Special Trig Limits, Example 33:55
- Special Trig Limits, Example 4: With More Degrees4:57
- Special Trig Limits, Example 56:21
10m 14s
- Intro0:00
- Definition0:06
- 3 Rules: f(x) Is Continuous…0:21
- Example 1: Finding Continuity1:06
- Types of Discontinuity2:44
- Jump2:52
- Point3:24
- Essential (Asymptote)3:47
- Removable4:17
- Example 2: Continuity Examples4:41
- Example 3: Continuity Examples6:13
- Example 4: Locate & Identify Type of Discontinuities8:00
6m 16s
- Intro0:00
- Problem 10:08
- Problem 21:51
- Problem 32:54
- Problem 44:31
4m 11s
- Intro0:00
- Definition0:09
- Formal Definition0:45
- Difference Quotient1:12
- Basic Derivatives1:16
- Differentiability2:54
7m 7s
- Intro0:00
- Basic Rules of Differentiation0:09
- Constant Rule0:14
- Constant Multiple Rule1:10
- Addition and Difference Rule1:40
- Example 1: Constant Rule2:25
- Example 2: Constant Multiple Rule3:01
- Example 3: Constant Multiple Rule3:35
- Example 4: Constant Rule4:34
- Example 5: Constant Multiple Rule5:03
- Example 65:33
7m 14s
- Intro0:00
- Power Rule0:07
- Power Rule Definition0:30
- Example 11:11
- Example 22:25
- Example 33:05
- Example 44:18
- Example 55:13
7m 53s
- Intro0:00
- Trigonometric Rules0:07
- COS X0:38
- Find Derivative1:02
- Example 12:46
- Example 2: COS Function3:09
- Example 3: Composite Expression3:54
- Example 4: Sec Function5:02
- Example 5: CSC5:33
- Example 6L COT6:42
11m 11s
- Intro0:00
- Product Rule0:07
- Definition0:20
- Example 10:43
- Example 22:11
- Example 34:24
- Example 45:24
- Example 56:42
- Example 67:51
16m 50s
- Intro0:00
- Quotient Rule0:07
- Definition0:30
- Example 11:17
- Example 2: With No X In Numerator2:49
- Example 34:30
- Example 4: With Decimals6:46
- Example 58:53
- Example 6: With Trig Functions12:55
19m 48s
- Intro0:00
- Chain Rule0:07
- Definition0:17
- Example 1: Applying the Chain Rule1:33
- Example 24:25
- Example 36:02
- Example 49:25
- Example 512:47
- Example 615:27
15m
- Intro0:00
- Types of Derivatives: Higher Order Derivatives0:07
- 1st Derivative / F Prime0:19
- 2nd Derivative0:25
- 3rd Derivative0:32
- Example 11:48
- Example 2: Find 3rd Derivative3:13
- Example 3: Acceleration4:25
- Example 410:20
- Example 5: 2nd Derivative12:11
13m 14s
- Intro0:00
- Types of Derivatives: Exponential Functions0:08
- Derivatives: Definition/ Formula0:28
- Example 11:25
- Example 22:47
- Example 34:13
- Example 47:11
- Example 59:23
- Example 611:06
11m 30s
- Intro0:00
- Types of Derivatives: Logarithmic Functions0:06
- Rule for Logarithmic Functions0:28
- Example 10:58
- Example 23:10
- Example 34:38
- Example 47:18
- Example 58:48
- Example 69:38
16m 54s
- Intro0:00
- Types of Derivatives: Inverse Trigonometric Functions0:06
- 6 Fundamental Properties of Inverse Trigonometric Functions0:38
- Example 12:17
- Example 23:41
- Example 35:37
- Example 47:24
- Example 510:08
16m 53s
- Intro0:00
- Implicit Differentiation: First Order0:07
- Example 1: Setting Up0:45
- Example 1: Solving1:41
- Implicit Differentiation: Second Order (Ex. 2)4:55
- Example 3: Implicit Differentiation9:11
- Example 4: Implicit Differentiation9:56
- Example 5: Implicit Differentiation With Double Derivative12:46
11m 7s
- Intro0:00
- Practice Problem 10:09
- Answer3:24
- Practice Problem 23:36
- Answer6:29
- Practice Problem 36:42
- Answer8:39
- Practice Problem 48:43
- Answer9:33
- Practice Problem 59:41
- Answer10:40
22m 36s
- Intro0:00
- Tangent and Normal Lines0:10
- Definition0:22
- Example 10:55
- Tangent and Normal Lines: Example 22:43
- Tangent and Normal Lines5:21
- Example 35:35
- Tangent and Normal Lines: Example 49:14
- Tangent and Normal Lines: Example 512:27
- Tangent and Normal Lines: Example 615:54
- Tangent and Normal Lines: Example 719:05
18m 42s
- Intro0:00
- Position, Velocity, and Acceleration0:10
- Position Function0:14
- Velocity Function0:34
- Acceleration Function1:01
- Example 11:20
- Example 26:31
- Example Continue: Velocity When Acceleration is Zero6:32
- Example 3: Where Is Particle Changing Directions?8:16
- Example 4: Total Distance Traveled From 0 to 2 Second11:09
- Example 5: Ball Drop Problem16:40
26m 22s
- Intro0:00
- Related Rates0:06
- Finding Rate of Change: Organization & Big Picture0:23
- Example 2: Area of a Circle1:17
- Example 3: Spherical Volume Expanding4:19
- Example 4: Traveling Problem7:57
- Example 5: Square Increase12:37
- Example 6: Standard Related Rates Problem16:59
- Example 7: Standard Related Rates Problem19:49
12m 22s
- Intro0:00
- Extrema: First Derivative Test0:09
- Example 10:46
- Example 2: Real World Application/ Cost Function4:05
- Example 3: Minimums & Maximums7:10
- Example 4: Find Critical Points10:52
11m 43s
- Intro0:00
- Concavity: Second Derivative Test0:06
- Definition0:34
- Example 10:54
- Example 22:51
- Example 34:08
- Example 45:52
8m 28s
- Intro0:00
- Rolle's Theorem0:07
- Conditions0:11
- Summary0:41
- Example 11:09
- Example 23:08
- Example 34:48
9m 39s
- Intro0:00
- Mean Value Theorem0:06
- Rolle's Theorem0:07
- Mean Value Theorem Conditions0:24
- Mean Value Theorem Definition0:36
- Example 10:56
- Example 22:44
- Example 35:28
- Example 47:15
12m 25s
- Intro0:00
- Differentials0:08
- 1st Differential Formula0:29
- 2nd Differential Formula0:57
- Example 11:06
- Example 23:21
- Example 35:49
- Example 47:19
- Example 59:06
13m 21s
- Intro0:00
- Practice Problem 10:10
- Answer1:57
- Practice Problem 22:08
- Answer5:39
- Practice Problem 35:45
- Answer9:59
- Practice Problem 410:12
- Answer11:49
- Practice Problem 511:52
- Answer13:00
10m 22s
- Intro0:00
- Practice Problem 10:10
- Slope1:30
- Tangent Line Equation2:17
- Absolute Minimum2:24
- 2 Possible X Points With Minimums3:15
- One Interest Point4:14
- Concavity4:33
- Positive Value = Positive Concavity4:10
- Minimum Point5:34
- Absolute Minimum6:18
- Point(s) of Inflection6:31
- Definition6:49
- 2 Points Of Inflection9:59
1m 8s
- Intro0:00
- Definition0:09
- Definition0:16
- Example0:20
8m 50s
- Intro0:00
- Power Rule0:06
- Example 10:25
- Example 22:02
- Example 32:54
- Example 43:45
- Example 54:49
- Example 66:47
9m 43s
- Intro0:00
- Basic Rules of Integration0:09
- Constant Rule0:22
- Example 10:40
- Addition and Difference Rule1:40
- Example 21:58
- Example 3: Subtraction/ Difference Rule2:47
- Example 43:55
- Example 55:19
- Example 67:37
8m 58s
- Intro0:00
- Trigonometric Rules0:09
- Integral of SIN0:38
- Example 1: Integral of SIN1:46
- Example 2: Integral of COS2:38
- Example 3: With 2 terms of X3:06
- Example 4: Integral of SEC4:15
- Example 5: Integral of CSC5:06
- Example 66:18
13m 59s
- Intro0:00
- Chain Rule0:07
- Example 10:37
- Example 23:17
- Example 35:09
- Example 47:53
- Example 59:40
- Example 611:39
12m 52s
- Intro0:00
- Types of Integrals: Exponential Functions0:09
- Rule 10:30
- Rule 20:49
- Example 11:11
- Example 22:54
- Example 34:19
- Example 45:19
- Example 57:37
- Example 69:04
13m
- Intro0:00
- Types of Integrals: Natural Log Functions0:09
- Example 10:49
- Example 22:06
- Example 34:01
- Example 45:37
- Example 57:30
- Example 69:05
8m 29s
- Intro0:00
- Types of Integrals: Inverse Trig Functions0:09
- One Property0:40
- Example 11:19
- Example 23:44
- Example 34:53
- Example 45:53
15m 37s
- Intro0:00
- Problem 10:09
- Answer4:09
- Problem 24:33
- Answer5:54
- Problem 35:59
- Answer8:02
- Problem 48:06
- Answer10:27
- Problem 510:43
- Answer14:46
15m 55s
- Intro0:00
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Properties0:10
- Definition of Integral0:49
- Example 11:14
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: Properties2:40
- Rule 12:50
- Rule 23:14
- Rule 33:33
- Rule 43:52
- Example 24:07
- Example 36:17
- Example 49:31
- Example 510:52
- Example 613:34
18m 34s
- Intro0:00
- Area Under Curve0:07
- Definition of Integral0:09
- Left Endpoint1:17
- Right Endpoint1:47
- Midpoints2:09
- Example 12:40
- Example 24:59
- Example 38:48
- Example 410:23
- Example 512:30
- Example 615:32
10m 35s
- Intro0:00
- Reimann Sums0:08
- Definition1:07
- Example 12:48
- Example 25:38
- Example 37:21
- Example 49:14
12m 46s
- Intro0:00
- The Trapezoid Rule0:09
- Definition: Area Of A Trapezoid0:26
- Terms of Formula1:35
- Example 12:11
- Example 24:29
- Example 37:22
- Example 410:01
11m 22s
- Intro0:00
- Mean Value Theorem of Integration0:06
- Example 10:53
- Example 22:29
- Example 33:48
- Example 46:02
4m 44s
- Intro0:00
- Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus0:07
- Definition0:39
- Example 11:08
- Example 22:07
- Example 32:48
- Example 43:23
16m 39s
- Intro0:00
- Example 10:10
- Example 23:00
- Example 34:46
- Example 48:22
- Example 511:04
- Example 613:09
21m 9s
- Intro0:00
- Revolving Solids Washer Disk Methods0:11
- Explanation0:33
- Formula3:12
- Example 13:42
- Example 26:54
- Example 39:29
- Example 412:16
- Example 515:35
26m 46s
- Intro0:00
- Revolving Solids: Cylindrical Shells Method0:09
- Volume Of A Solid0:25
- Formula2:51
- Example 12:56
- Example 27:28
- Example 311:39
- Example 417:36
- Example 521:45
27m 41s
- Intro0:00
- Revolving Solids Known Cross Sections0:08
- Example 10:35
- Example 26:01
- Example 311:03
- Example 417:29
- Example 522:19
17m 54s
- Intro0:00
- Differential Equations0:08
- Example 10:30
- Differential Equations: Euler's Method2:33
- Rules2:39
- Example 23:00
- Example 35:42
- Example 49:44
- Example 514:14
16m 30s
- Intro0:00
- Slope Fields0:08
- What Are Slope Fields0:21
- Example 10:42
- Example 26:30
- Example 311:17
14m 19s
- Intro0:00
- Practice Problem 10:10
- Answer3:46
- Practice Problem 23:49
- Answer6:20
- Practice Problem 36:26
- Answer8:02
- Practice Problem 48:07
- Answer10:58
- Practice Problem 511:05
- Answer14:06
9m 14s
- Intro0:00
- Problem 10:10
- Part A0:24
- Part A: Solution2:04
- Part B2:10
- Problem 1, Part B Continue2:23
- Part B: Solution6:15
- Problem 1, Part C6:58
- Part C: Solution12:40
- Problem 212:52
- Part A13:02
- Part A: Solution15:34
- Part B16:03
- Part B: Solution18:48
17m 50s
- Intro0:00
- Problem 10:20
- Problem 21:24
- Problem 32:53
- Problem 43:56
- Problem 58:18
- Problem 69:06
- Problem 710:14
- Problem 812:16
- Problem 914:13
17m 32s
- Intro0:00
- Problem 100:18
- Problem 112:26
- Problem 126:11
- Problem 137:04
- Problem 148:06
- Problem 1510:32
- Problem 1611:40
- Problem 1713:00
- Problem 1814:43
22m 14s
- Intro0:00
- Problem 190:21
- Problem 202:33
- Problem 217:23
- Problem 2210:24
- Problem 2312:18
- Problem 2413:13
- Problem 2515:52
- Problem 2617:03
- Problem 2719:44
19m 35s
- Intro0:00
- Problem 280:23
- Problem 293:50
- Problem 305:31
- Problem 319:02
- Problem 3210:07
- Problem 3311:27
- Problem 3413:47
- Problem 3515:21
- Problem 3616:53
25m 43s
- Intro0:00
- Problem 370:22
- Problem 382:27
- Problem 395:36
- Problem 407:21
- Problem 4110:08
- Problem 4211:29
- Problem 4313:07
- Problem 4418:18
- Problem 4521:08
16m 50s
- Intro0:00
- Problem 1, Part A0:20
- Problem 1, Part B3:03
- Problem 1, Part C4:11
- Problem 1, Part D5:36
- Problem 2, Part A7:37
- Problem 2, Part B9:02
- Problem 2, Part C12:31
21m 36s
- Intro0:00
- Problem 3, Part A0:18
- Problem 3, Part B5:57
- Problem 4, Part A11:26
- Problem 4, Part B12:28
- Problem 4, Part C15:35
- Problem 4, Part D18:56
13m 39s
- Intro0:00
- Problem 5, Part A0:21
- Problem 5, Part B3:07
- Problem 5, Part C6:43
- Problem 68:24
For more information, please see full course syllabus of Calculus AB
Calculus AB Position Velocity & Acceleration
In this lesson, Professor John Zhu gives an introduction to position, velocity and acceleration. He explains the position function, velocity function and acceleration function. He then shows you several example problems.
Share this knowledge with your friends!
Copy & Paste this embed code into your website’s HTML
Please ensure that your website editor is in text mode when you paste the code.(In Wordpress, the mode button is on the top right corner.)
- - Allow users to view the embedded video in full-size.








































 Raffi Hovasapian
Raffi Hovasapian John Zhu
John Zhu
 Answer Engine
Answer Engine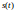 ,
, 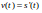 ,
, 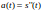





0 answers
Post by Florian Cagol on February 18, 2015
How would you solve for the value of "t" when "v" attains its maximum ?